import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs'; import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
Adding a comment
Principle
Sipmon allows us to add comments on an object. This comment is visible by anyone having access to the resource (host or service). A comment has the following properties:
- Hostname
- Servicename if the comment is associated with a service
- Date of entry of the comment
- Author of the comment
- The contents of the comment
- The validity of the comment against a restart of the scheduler
Practice
There are two solutions to add a comment:
The following window appears:
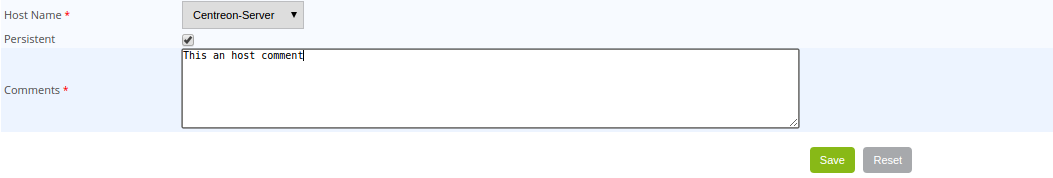
- The Host Name field defines the host concerned by the comment.
- If you have chosen to add a comment to a service, the Service field can be used to select the service concerned by the comment.
- If the Persistent box is checked, the comment will be maintained in the event of a restart of the scheduler.
- The Comments field contains the comment itself.
Management of checks
Principle
It is possible to temporarily enable or disable check on a host or a service.
Changes to settings checks do not affect the configuration of the object in the database. These changes are made on the monitoring in real time, they are canceled if the scheduler is restarted.
Practice
Management of notifications
Principle
It is possible to temporarily enable or disable the notification of a host or a service.
Changes the notifications settings do not affect the configuration of the object in the database. These changes are made on the real time monitoring, they are canceled if the scheduler is restarted.
Practice
There are two ways of managing the notifications:
Reprogramming checks
Principle
By default, the checks (checks on a service) are executed at regular intervals following the configuration defined by the user. It is possible to interact on the check scheduling pile to change the programming of the checks.
There are two types of programming:
- Normal programming: the service check is given priority in the scheduler queue (asap).
- Forced programming: the service check is given priority in the scheduler queue (asap) even if the time of the execution request is outside the check period or if the service is not of the active type.
Practice
There are two ways of forcing the check of a service: