import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs'; import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
Tables of network flows
Tables of network flows to integrate monitoring platform to IT
Central server
| From | To | Protocol | Port | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central server | NTP server | NTP | UDP 123 | Synchronization of the system clock |
| Central server | DNS server | DNS | UDP 53 | Domain name resolution |
| Central server | SMTP server | SMTP | TCP 25 | Notification via email |
| Central server | LDAP(s) server | LDAP(s) | TCP 389 (636) | Authentication to access the Sipmon web interface |
| Central server | DBMS server | MySQL | TCP 3306 | Access to Sipmon databases (if deported to a dedicated server) |
| Central server | HTTP Proxy | HTTP(s) | TCP 80, 8080 (443) | If your platform needs to connect to a web proxy to access the Sipmon IT Edition |
| Central server | Repository | HTTP (FTP) | TCP 80 (FTP 20) | Repository for system and application packages |
Poller
| From | To | Protocol | Port | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poller | NTP server | NTP | UDP 123 | Synchronization of the system clock |
| Poller | DNS server | DNS | UDP 53 | Domain name resolution |
| Poller | SMTP server | SMTP | TCP 25 | Notification via email |
| Poller | Repository | HTTP (FTP) | TCP 80 (FTP 20,21) | Repository for system and application packages |
Remote Server
| From | To | Protocol | Port | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Server | NTP server | NTP | UDP 123 | Synchronization of the system clock |
| Remote Server | DNS server | DNS | UDP 53 | Domain name resolution |
| Remote Server | SMTP server | SMTP | TCP 25 | Notification via email |
| Remote Server | LDAP(s) server | LDAP(s) | TCP 389 (636) | Authentication to access the Sipmon web interface |
| Remote Server | DBMS server | MySQL | TCP 3306 | Access to Sipmon databases (if deported to a dedicated server) |
| Remote Server | Repository | HTTP (FTP) | TCP 80 (FTP 20) | Repository for system and application packages |
Other flows can be necessary for Sipmon web authentication (RADIUS, etc.) or notification system defined.
Tables of platform flows
Poller
| From | To | Protocol | Port | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central server | Poller | ZMQ | TCP 5556 | Export of Sipmon configuration (depending on communication type) |
| Central server | Poller | SSH (legacy) | TCP 22 | Export of Sipmon configuration (depending on communication type) |
| Poller | Central server | BBDO | TCP 5669 | Transfer of collected data |
| Poller | Central server | HTTP(S) | TCP 80 (443) | Poller registration |
Remote Server
| From | To | Protocol | Port | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central server | Remote Server | ZMQ | TCP 5556 | Export of Sipmon configuration |
| Remote Server | Central server | BBDO | TCP 5669 | Transfer of collected data |
| Remote Server | Central server | HTTP(S) | TCP 80 (443) | Remote Server registration |
| Remote Server | Poller | ZMQ | TCP 5556 | Export of Sipmon configuration (depending on communication type) |
| Remote Server | Poller | SSH (legacy) | TCP 22 | Export of Sipmon configuration (depending on communication type) |
| Poller | Remote Server | BBDO | TCP 5669 | Transfer of collected data |
| Poller | Remote Server | HTTP(S) | TCP 80 (443) | Poller registration |
If Remote Server is not used as proxy for a Poller, Poller network flows apply.
Monitoring
| From | To | Protocol | Port | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poller | Network equipment, servers, etc. | SNMP | UDP 161 | Monitoring |
| Network equipment | Poller | Trap SNMP | UDP 162 | Monitoring |
| Poller | Servers | NRPE | TCP 5666 | Monitoring |
| Poller | Servers | NSClient++ | TCP 12489 | Monitoring |
If the Sipmon server is a poller too, do not forget to open monitoring flows.
Other flows can be necessary to monitor databases, access to API, or application ports.
Users and groups
This information pertains to the Red Hat / CentOS system. Names of users, groups and services can change according to the GNU/Linux distribution.
Description of software and linked users:
Description of optional software and linked users:
| Software | Service | User | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sipmon VMware | Sipmon_vmware | Sipmon | not installed by default |
| RRDtool | rrdcached | rrdcached | not enabled and not defined in Sipmon by default |
Description of groups and linked users for Sipmon Open Source and IT Edition:
| Group | Users |
|---|---|
| apache | nagios,Sipmon,Sipmon-gorgone |
| Sipmon | Sipmon-engine,Sipmon-broker,apache,Sipmon-gorgone |
| Sipmon-broker | Sipmon,nagios,Sipmon-engine,apache,Sipmon-gorgone |
| Sipmon-engine | Sipmon-broker,apache,nagios,Sipmon,Sipmon-gorgone |
| Sipmon-gorgone | Sipmon,apache,Sipmon-gorgone,Sipmon-engine,Sipmon-broker |
| rrdcached | Sipmon-broker,apache |
Description of groups and linked users for Sipmon Business Edition:
| Group | Users |
|---|---|
| apache | nagios,SipmonBI,Sipmon,Sipmon-gorgone |
| Sipmon | Sipmon-engine,Sipmon-broker,apache,rrdcached,SipmonBI,Sipmon-gorgone |
| Sipmon-broker | Sipmon,nagios,Sipmon-engine,apache,rrdcached,Sipmon-gorgone |
| Sipmon-engine | Sipmon-broker,apache,nagios,Sipmon,Sipmon-gorgone |
| Sipmon-gorgone | Sipmon,apache,Sipmon-gorgone,Sipmon-engine,Sipmon-broker |
| SipmonBI | apache |
| Sipmon-map | |
| mysql | SipmonBI |
Description of users, umask and home directory for Sipmon Open Source and IT Edition:
| User | umask | home | Shell |
|---|---|---|---|
| root | 0022 | /root | /bin/bash |
| apache | 0022 | /var/www | /sbin/nologin |
| Sipmon | 0002 | /var/spool/Sipmon | /bin/bash |
| Sipmon-broker | 0002 | /var/lib/Sipmon-broker | /bin/bash |
| Sipmon-engine | 0002 | /var/lib/Sipmon-engine | /bin/bash |
| Sipmon-gorgone | 0002 | /var/lib/Sipmon-gorgone | /bin/bash |
| mysql | 0002 | /var/lib/mysql | /sbin/nologin |
| rrdcached | 0002 | /var/rrdtool/rrdcached | /bin/bash |
Description of users, umask and home directory for Sipmon Business Edition:
| User | umask | home | Shell |
|---|---|---|---|
| root | 0022 | /root | /bin/bash |
| apache | 0022 | /var/www | /sbin/nologin |
| Sipmon | 0002 | /var/spool/Sipmon | /bin/bash |
| SipmonBI | 0002 | /home/SipmonBI | /bin/bash |
| Sipmon-agent | 0002 | /var/lib/Sipmon-agent | /bin/bash |
| Sipmon-broker | 0002 | /var/lib/Sipmon-broker | /bin/bash |
| Sipmon-engine | 0002 | /var/lib/Sipmon-engine | /bin/bash |
| Sipmon-gorgone | 0002 | /var/lib/Sipmon-gorgone | /bin/bash |
| Sipmon-map | 0002 | /home/Sipmon-map | /bin/bash |
| mysql | 0002 | /var/lib/mysql | /sbin/nologin |
| rrdcached | 0002 | /var/rrdtool/rrdcached | /bin/bash |
Software dependencies
For your information, the following table describes the software dependencies. Everything comes prepackaged with Sipmon, you do not have to install anything manually.
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| Apache | 2.4 |
| GnuTLS | >= 2.0 |
| Net-SNMP | 5.7 |
| openssl | >= 1.0.1k |
| PHP | 8.1 |
| RRDtools | 1.4.7 |
| zlib | 1.2.3 |
Architectures
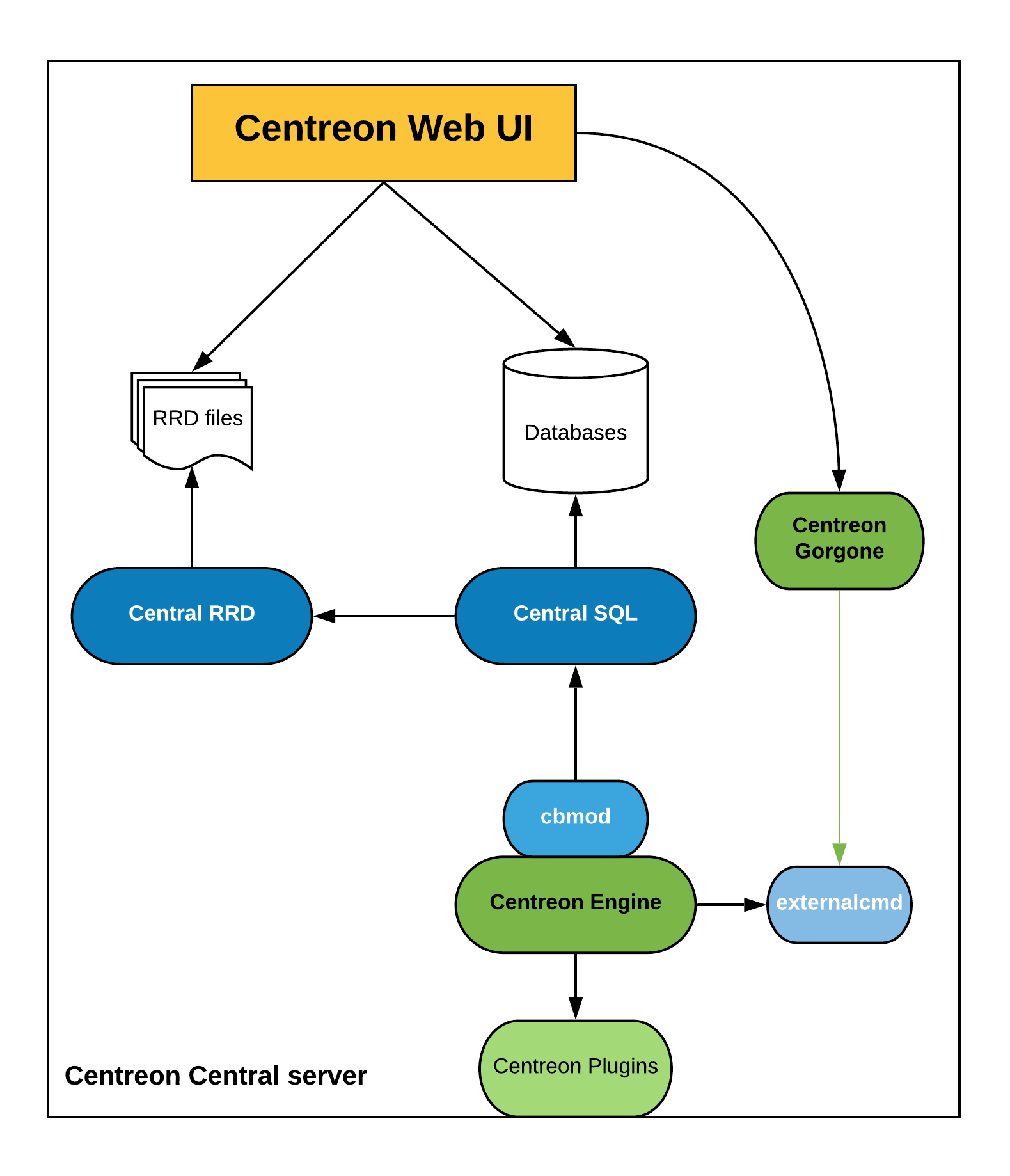
Standalone central server
If you are not monitoring many hosts, you may only need one central server.
Components
The following components are used in a central server:
- Apache web server for the Sipmon web interface
- MariaDB databases to store Sipmon configuration parameters as well as monitoring and performance data
- A monitoring engine to collect data
- Collected data are sent to Sipmon Broker SQL using cbmod by the monitoring engine
- Sipmon Broker SQL stores information into MariaDB databases and forwards them to Sipmon Broker RRD
- Sipmon Broker RRD generates and updates RRD files with data in order to display performance graphs
Architecture
The diagram below summarizes how a central server works:
Distributed architecture
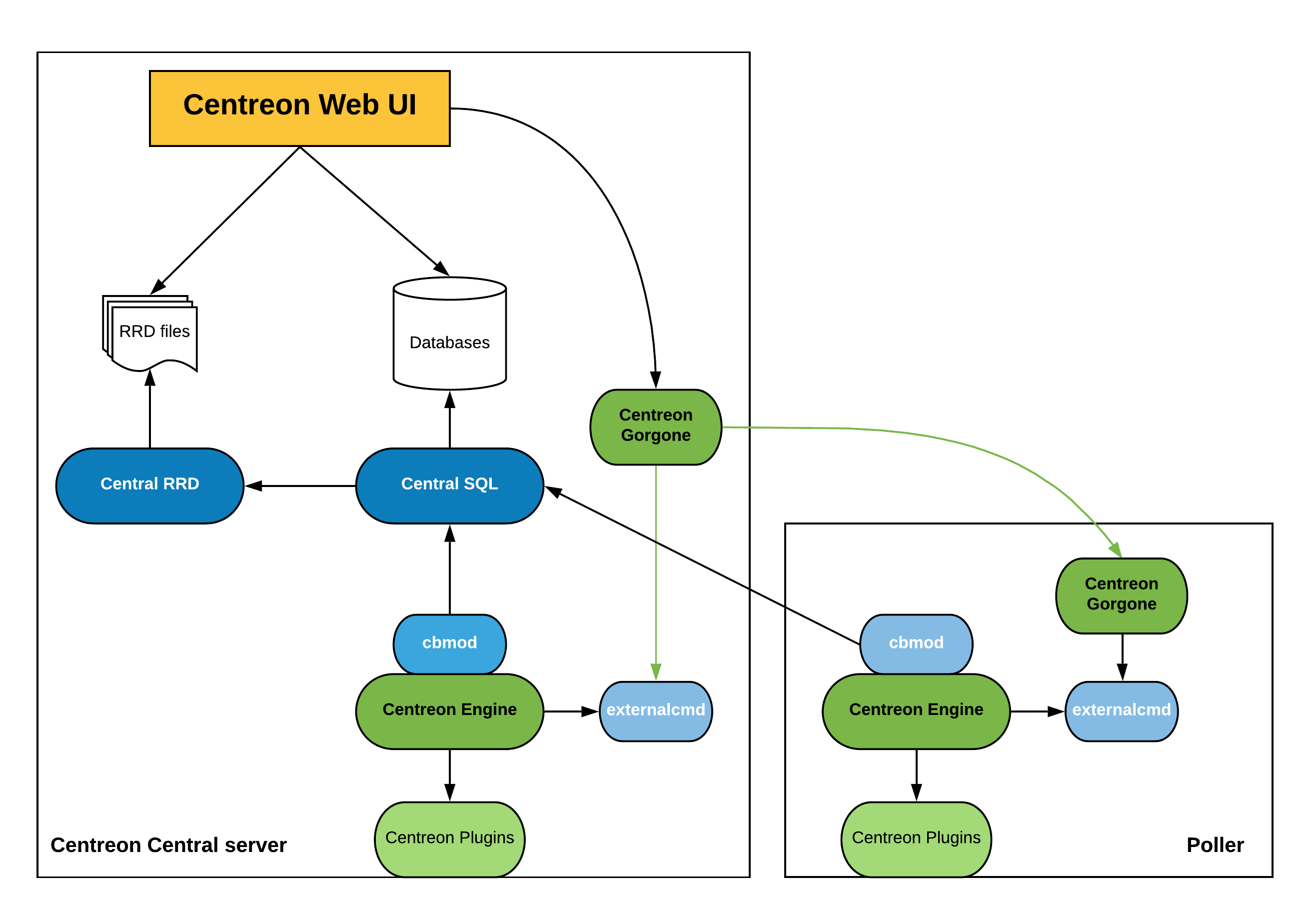
Description (Distributed)
The distributed architecture has the following elements:
- A central Sipmon server to display information
- One or more remote servers and/or pollers to collect data
The central Sipmon server includes the following items:
- Sipmon web interface
- Databases (MariaDB + RRD)
- Monitoring Engine
- Broker
The Poller includes the following items:
- Monitoring Engine
- Broker module to forward collected data to a central broker
This architecture is used for:
- Enable load balancing across multiple remote monitoring servers
- Network streams isolation: if your monitoring architecture have to monitor a DMZ area, it is easier (and safe) to place a remote server in the DMZ network
Components
Central Sipmon server
Many components are used to build a central Sipmon server:
- Apache web server for Sipmon web interface
- MariaDB databases to store Sipmon configuration parameters as well as monitoring and performance data
- The Sipmon Gorgone process is used to send monitoring configuration to the remote server and to manage it
- A monitoring engine to collect data
- Collected data are sent to Sipmon Broker SQL using cbmod by monitoring engine
- Sipmon Broker SQL allows to store information into MariaDB databases and forward them to Sipmon Broker RRD
- Sipmon Broker RRD generates and updates RRD files with data in order to display performance graphs
Poller
Many components are used to build a poller:
- A monitoring engine to collect data
- Collected data are sent to Sipmon Broker SQL using cbmod by monitoring engine
Architecture
The diagram below summarizes the architecture:
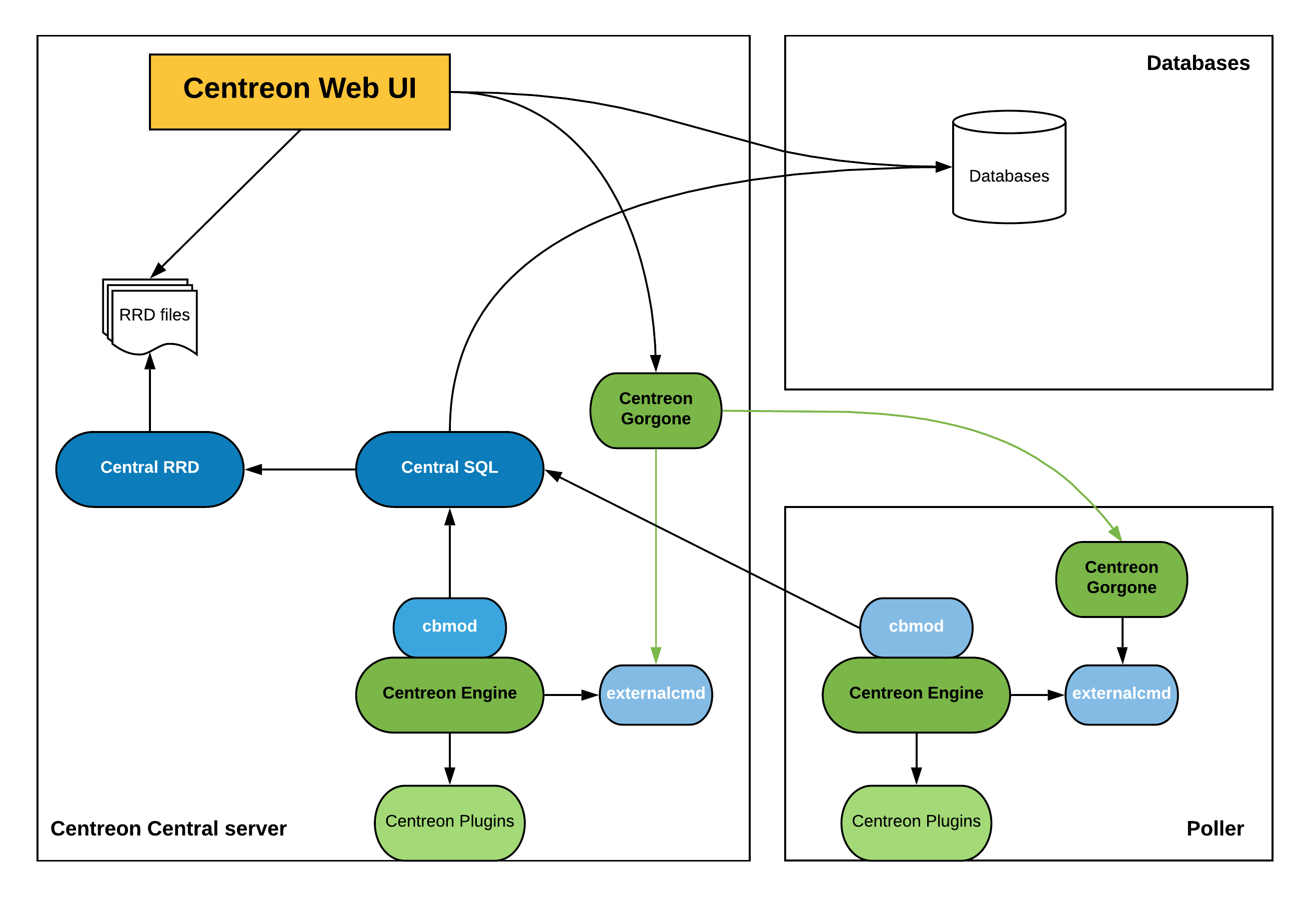
Remote DBMS
The distributed architecture with remote DBMS is to have three types of entities:
- A central Sipmon server to display information
- A DBMS server to store collected data
- One or more remote servers to collect data
The central Sipmon server includes the following items:
- Sipmon web interface
- Monitoring Engine
- Broker
- RRD files
The DBMS server store information into MariaDB databases.
The poller includes the following items:
- Monitoring Engine
- Broker module to forward collected data to a central broker
This architecture is used for:
- Enable load balancing across multiple remote monitoring servers
- Network streams isolation: if your monitoring architecture have to monitor a DMZ area, it is easier (and safe) to place a remote server in the DMZ network
- Have a remote DBMS
Components
DBMS server
The DBMS server is used only to store Sipmon configuration parameters as well as monitoring and performance data into MariaDB databases
Central Sipmon server
Many components are used to build a central Sipmon server:
- Apache web server for Sipmon web interface
- The central Sipmon server get configuration and collected data from DBMS server
- The Sipmon Gorgone process is used to send monitoring configuration to the remote server and to manage it
- A monitoring engine to collect data
- Collected data are sent to Sipmon Broker SQL using cbmod by monitoring engine
- Sipmon Broker SQL allows to store information into MariaDB databases and forward them to Sipmon Broker RRD
- Sipmon Broker RRD generates and updates RRD files with data in order to display performance graphs
Poller
Many components are used to build a poller:
- A monitoring engine to collect data
- Collected data are sent to Sipmon Broker SQL using cbmod by monitoring engine
Architecture
The diagram below summarizes the architecture:
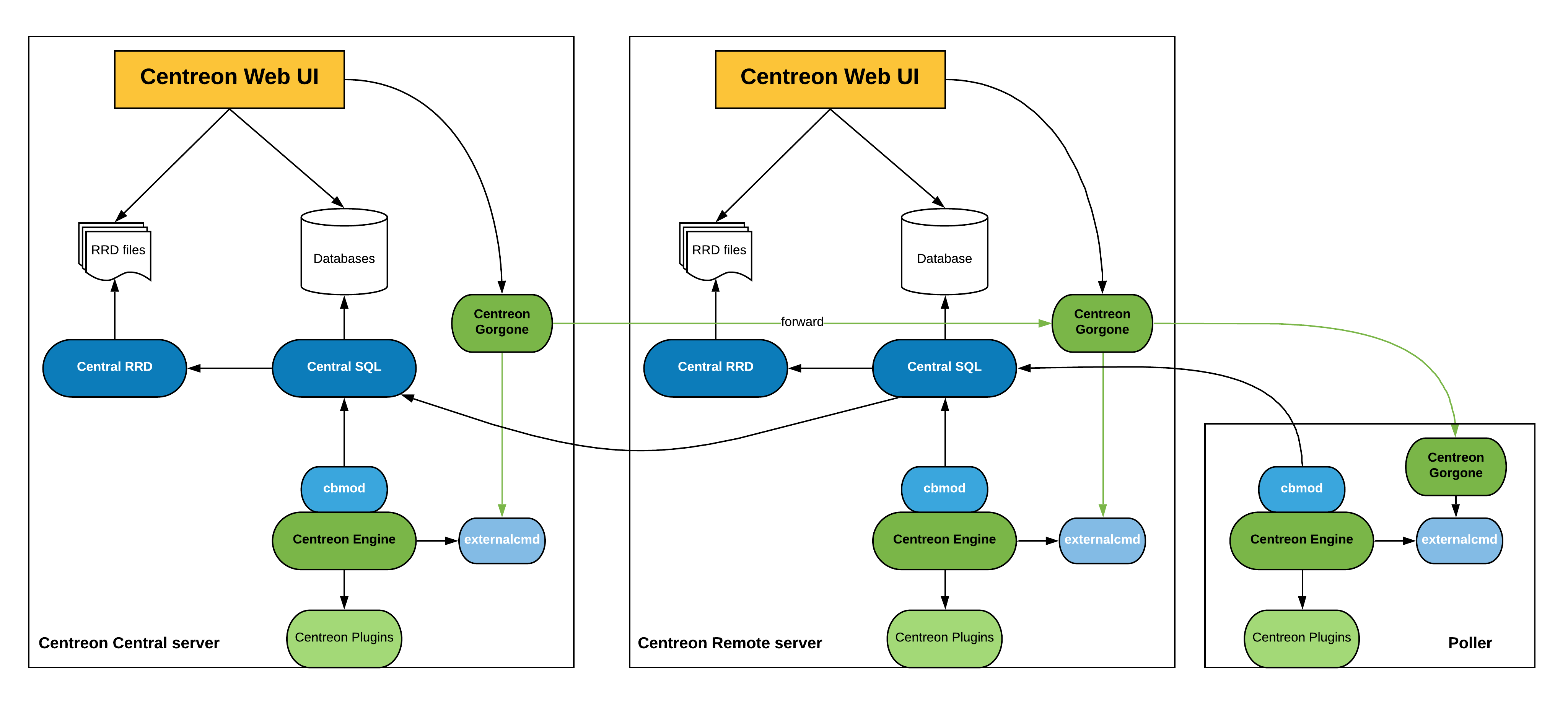
Remote Server
The distributed architecture with Remote sever is to have three types of entities:
- A Sipmon Central server to configure monitoring and to display & operate on collected data
- One or more Sipmon Remote server to display & operate on a subset of collected data
- One or more pollers to collect data
The central Sipmon server includes the following items:
- Sipmon web interface(configure, display & operate)
- Monitoring Engine
- Broker
- Databases (MariaDB + RRD)
The Remote servers include the following items:
- Sipmon web interface (display & operate a subset of data)
- Monitoring Engine
- Databases (MariaDB + RRD)
- Broker module to forward collected data to a central broker
This architecture is used for:
- Enable load balancing across multiple remote monitoring servers
- Network streams isolation: if your monitoring architecture has to monitor a DMZ area, it is easier (and safe) to place a remote server in the DMZ network
- Have dedicated webinterface to display & operate on a subset of data.
Components
Central Sipmon server
Many components are used to build a Sipmon server:
- Apache web server for Sipmon web interface
- MariaDB databases to store Sipmon configuration parameters as well as monitoring and performance data
- The Sipmon Gorgone process is used to send monitoring configuration to the remote server and to manage it
- A monitoring engine to collect data
- Collected data are sent to Sipmon Broker SQL using cbmod by monitoring engine
- Sipmon Broker SQL allows to store information into MariaDB databases and forward them to Sipmon Broker RRD
- Sipmon Broker RRD generates and updates RRD files with data in order to display performance graphs
Remote monitoring server
Many components are used to build a remote server:
- Apache web server for Sipmon web interface
- MariaDB databases to store monitoring and performance data
- The Sipmon Gorgone process is used to operate on collected data
- A monitoring engine to collect data
- Collected data are sent to Sipmon Broker SQL using cbmod by monitoring engine
- Sipmon Broker SQL allows to store information into MariaDB databases and forward them to Sipmon Broker RRD locally. All information are forwarded to the Sipmon central server.
- Sipmon Broker RRD generates and updates RRD files with data in order to display performance graphs
Poller
Many components are used to build a poller:
- A monitoring engine to collect data
- Collected data are sent to Sipmon Broker SQL using cbmod by monitoring engine
Architecture
The diagram below summarizes the architecture: